Copying Data
Steven J. Zeil
Copying data is one of the most common operations in C++.
-
Every time we write an assignment
x = y;we are copying data.
-
As our data gets more complicated, so does copying.
But, First…
A slight diversion …
1 Destructors
Destructors are used to clean up objects that are no longer in use.
-
A destructor for a class C is a function named ~C
- This function takes no parameters
-
The most common action within a destructor is deleting pointers
1.1 Destructors are Never Called Explicitly
The compiler generates all calls to destructors implicitly
-
when a variable goes out of scope,
-
or when we delete a pointer.
Implicit Destructor Call 1
If we write
void foo (int d, int c)
{
Money m (d,c);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
Money mon2 = m;
⋮
}
}
the compiler generates
void foo (int d, int c)
{
Money m (d,c);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
Money mon2 = m;
⋮
mon2.~Money();
}
m.~Money();
}
Implicit Destructor Call 2
If we write
void foo (int d, int c)
{
Money* m = new Money (d,c);
⋮
delete m;
}
the compiler generates
void foo (int d, int c)
{
Money* m = new Money (d,c);
⋮
m->~Money();
free(m);
}
A Typical Destructor
We use destructors to clean up data “owned” by our structured types:
class BidCollection {
int MaxSize;
int size;
Bid* elements; // array of bids
public:
BidCollection (int MaxBids = 1000);
~BidCollection ();
⋮
Implementing the Destructor
The destructor would be implemented as
BidCollection::~BidCollection()
{
delete [] elements;
}
Compiler-Provided Destructors
If you don’t provide a destructor for a class, the compiler generates one for you automatically.
- The automatically generated destructor simply invokes the destructors for any data member objects.
-
If none of the members have programmer-supplied destructors, then the overall effect is to do nothing.
-
A Compiler-Generated Destructor
- We have not declared or implemented a destructor for our Time class,
#ifndef TIMES_H
#define TIMES_H
#include <iostream>
/**
* Times in this program are represented by three integers: H, M, & S, representing
* the hours, minutes, and seconds, respecitvely.
*/
class Time {
public:
// Create time objects
Time(); // midnight
Time (int h, int m, int s);
// Access to attributes
int getHours() const;
int getMinutes() const;
int getSeconds() const;
// Calculations with time
void add (Time delta);
Time difference (Time fromTime);
/**
* Read a time (in the format HH:MM:SS) after skipping any
* prior whitepace.
*/
void read (std::istream& in);
/**
* Print a time in the format HH:MM:SS (two digits each)
*/
void print (std::ostream& out) const;
// Comparison operators
bool operator== (const Time&) const;
bool operator< (const Time&) const;
private:
// From here on is hidden
int secondsSinceMidnight;
};
inline
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& out, const Time& t)
{
t.print(out);
return out;
}
inline
bool operator!= (const Time& t1, const Time& t2)
{
return !(t1 == t2);
}
inline
bool operator> (const Time& t1, const Time& t2)
{
return t2 < t1;
}
inline
bool operator<= (const Time& t1, const Time& t2)
{
return !(t1 > t2);
}
inline
bool operator>= (const Time& t1, const Time& t2)
{
return !(t1 < t2);
}
#endif // TIMES_H
-
That’s OK
-
We have not declared a destructor for our Bid class
#ifndef BIDS_H
#define BIDS_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "time.h"
#include "money.h"
//
// Bids Received During Auction
//
class Bid {
std::string bidderName;
Money amount;
std::string itemName;
Time bidPlacedAt;
public:
Bid (std::string bidder, double amt,
std::string item, Time placedAt);
Bid();
// Access to attribute
std::string getBidder() const {return bidderName;}
double getAmount() const {return amount;}
std::string getItem() const {return itemName;}
Time getTimePlacedAt() const {return bidPlacedAt;}
// Print a bid
void print (std::ostream& out) const;
// Comparison operators
bool operator== (const Bid&) const;
bool operator< (const Bid&) const;
};
inline
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& out, const Bid& b)
{
b.print(out);
return out;
}
#endif
- Again that’s OK
- Despite the fact that the strings may need cleanup.
The compiler-generated destructor for
Bidinvokes the destructors for the data members, including those strings.
- Despite the fact that the strings may need cleanup.
Trusting the Compiler-generated Destructor
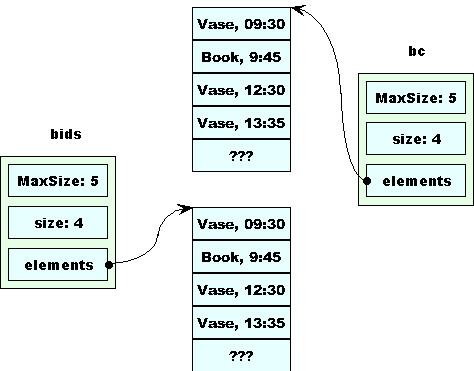
What would happen if we trusted the compiler-generated destructor for BidCollection?
Compiler-generated destructors are wrong when…
The compiler-generated destructor will leak memory when
-
Your ADT has pointers among its data members, and
-
Your ADT objects do not share those pointers with other objects.
Under those circumstances, the compiler-generated destructor will cause you program to leak memory.
The fix is to implement your own destructor for such classes, and explicitly clean up your mess on the heap:
void NidCollection::~BidCollection()
{
delete [] elements;
}
2 Copy Constructors
The copy constructor for a class Foo is the constructor of the form:
Foo (const Foo& oldCopy);
2.1 Where Do We Use a Copy Constructor?
The copy constructor gets used in 5 situations:
-
When you declare a new object as a copy of an old one:
Time time2 (time1);Time time2 = time1; -
When a function call passes a parameter “by copy” (i.e., the formal parameter does not have a &):
void foo (Time b, int k); ⋮ Time noon (12, 0, 0); foo (noon, 0); // foo actually gets a copy of noon -
When a function returns an object:
Time foo (int k); { Time t (k, 0, 0); ⋮ return t; } -
When explicitly invoked in another constructor’s initialization list:
Name (string gName, string sName) : givenName(gName), surName(sName) {} -
When an object is a data member of another class for which the compiler has generated its own copy constructor.
2.2 Compiler-Generated Copy Constructors
If we do not create a copy constructor for a class, the compiler generates one for us.
- copies each data member via their individual copy constructors.
-
For primitive types (int, double, pointers, etc.), just copies the bits.
-
2.3 Example: Bid: Compiler-Generated Copy Constructor
struct Bid {
std::string bidderName;
Money amount;
std::string itemName;
Time bidPlacedAt;
};
Bid does not provide a copy constructor, so the compiler generates one for us, just as if we had written:
struct Bid {
std::string bidderName;
Money amount;
std::string itemName;
Time bidPlacedAt;
Bid (const Bid&);
};
⋮
Bid::Bid (const Bid& b)
: bidderName(b.bidderName), amount(b.amount),
itemName(b.itemName), bidPlacedAt(b.bidPlacedAt)
{}
and that’s probably just fine.
2.4 Example: BidCollection: Compiler-Generated Copy Constructor
struct BidCollection {
int MaxSize;
int size;
Bid* elements; // array of bids
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of bids
*/
BidCollection (int MaxBids = 1000);
~BidCollection ();
/**
* Read all bids from the indicated file
*/
void readBids (std::string fileName);
};
BidCollection does not provide a copy constructor, so the compiler generates one for us, just as if we had written:
struct BidCollection {
int MaxSize;
int size;
Bid* elements; // array of bids
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of bids
*/
BidCollection (int MaxBids = 1000);
BidCollection (const BidCollection&);
};
⋮
BidCollection::BidCollection (const BidCollection& bc)
: MaxSize(bc.MaxSize), size(bc.size),
elements(bc.elements)
{}
which is not good at all!
Example: BidCollection is hard to copy
To see why, suppose we had some application code:
BidCollection removeEarly (BidCollection bc, Time t)
{
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}
return bc;
}
⋮
BidCollection afterNoonBids =
removeEarly (bids, Time(12,0,0));
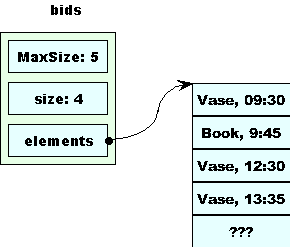
Assume we start with this in bids.
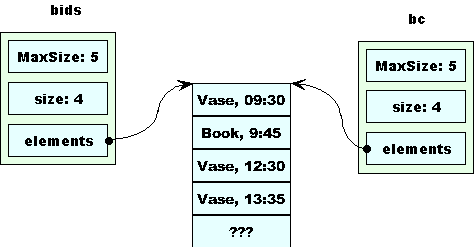
When removeEarly is called, we get a copy of bids .
BidCollection removeEarly (BidCollection bc, Time t)
{
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}
return bc;
}
⋮
BidCollection afterNoonBids = removeEarly (bids, Time(12,0,0));
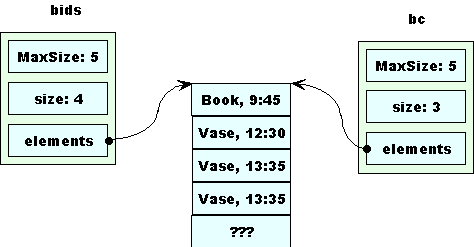
removeEarly removes the first morning bid from bc.
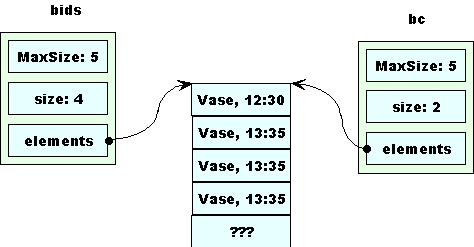
Then removeEarly removes the remaining morning bid from bc.
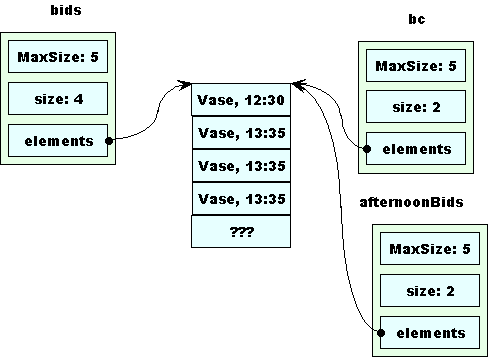
The return statement makes a copy of bc, which is stored in afterNoonBids
Trouble: bids is corrupted

Note that we have corrupted the original collection, bids
-
It thinks it has more (according to
size) bids than are left in the array -
The bids that it has are now changed
That’s not the worst of it!
When we exit removeEarly,
BidCollection removeEarly (BidCollection bc, Time t)
{
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}
return bc;
}
the destructor for BidCollection is called on bc
BidCollection::~BidCollection()
{
delete [] elements;
}

Taking us from this …
What a Mess!
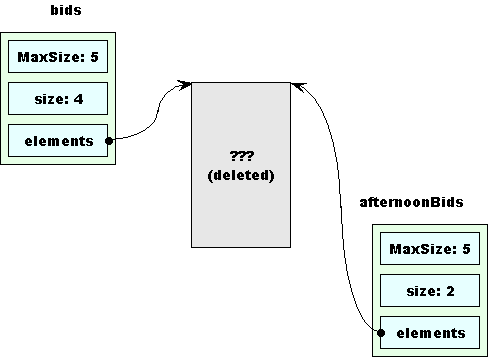
… to this.
Both collections have “dangling pointers”
Avoiding this Problem
We could
-
Decide never to pass a
BidCollectionby copy, never return one from a function, never to create a newBidCollectionas a copy of an old one.-
We would have to remember this decision in all future applications.
-
-
or, write our own copy constructor that actually works
-
Every
BidCollectionshould have its own unique array
-
2.5 Writing a BidCollection Copy Constructor
BidCollection::BidCollection (const BidCollection& bc)
: MaxSize (bc.MaxSize), size (bc.size)
{
elements = new Bid[MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
Once More, With Feeling!

With this copy constructor in place, things should go much more smoothly.
BidCollection removeEarly (BidCollection bc, Time t)
{
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}
return bc;
}
⋮
BidCollection afterNoonBids =
removeEarly (bids, Time(12,0,0));

When removeEarly is called, we get a copy of bids.
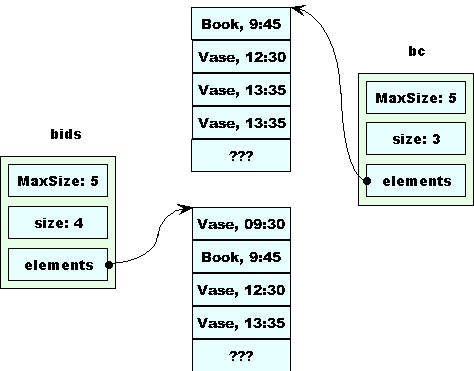
removeEarly removes the first morning bid from bc.
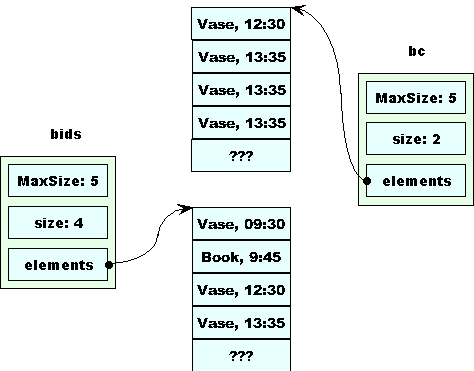
Then removeEarly removes the remaining morning bid from bc.
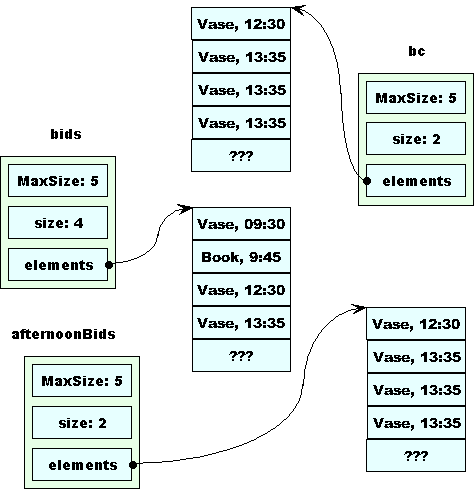
The return statement makes a copy of bc, which is stored in afterNoonBids.
But our new copy constructor actually creates a new array for afterNoonBids, copying the bids from bc’s array.
Much Nicer
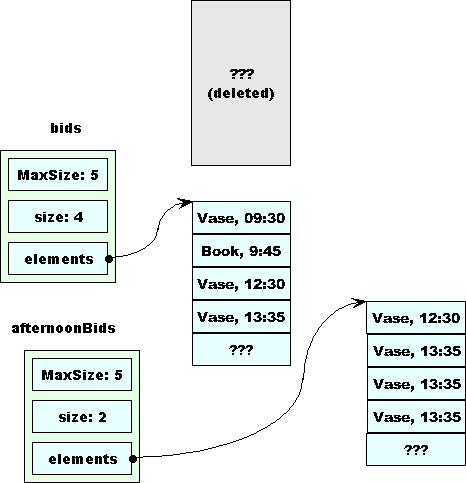
The destructor for BidCollection is called on bc
- Both remaining collections are OK.
2.6 Shallow & Deep Copying
If We Never Write Our Own
If our data members do not have explicit copy constructors (and their data members do not have explicit copy constructors, and … )
- then the compiler-provided copy constructor amounts to a bit-by-bit copy.
Shallow vs Deep Copy
Copy operations are distinguished by how they treat pointers:
-
In a shallow copy, all pointers are copied.
-
Leads to shared data on the heap.
-
-
In a deep copy, objects pointed to are copied, then the new pointer set to the address of the copied object.
-
Copied objects keep exclusive access to the things they point to.
-
Shallow copy is wrong when…
-
Your ADT has pointers among its data members, and
-
You don’t want to share the objects being pointed to.
Compiler-generated copy constructors are wrong when…
-
Your ADT has pointers among its data members, and
-
You don’t want to share the objects being pointed to.
3 Assignment
Copy constructors are not the only way we make copies of data.
-
Even more common is the use of assignment:
time2 = time1; -
Assignment is so common that it can be hard to imagine programming without it
-
though in rare conditions we will do so
-
E.g., you cannot assign
istreams andostreams -
You cannot copy them by constructor either
-
-
-
So the compiler will try to be helpful again
3.1 Compiler-Generated Assignment Ops
If you don’t provide your own assignment operator for a class, the compiler generates one automatically.
-
assigns each data member in turn.
-
If none of the members have programmer-supplied assignment ops, then this is a shallow copy
Example: BidCollection: Guess what happens
Our BidCollection class has no assignment operator, so the code below uses the compiler-generated version.
Suppose we had some application code:
BidCollection bids;
⋮
BidCollection bc;
Time t (12, 0, 0);
bc = bids;
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}
BidCollection bc;
Time t (12, 0, 0);
bc = bids;
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}

Assume we start with this in bids.

After the assignment, we have copied bids, bit-by-bit, into bc.
BidCollection bc;
Time t (12, 0, 0);
bc = bids;
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}

We remove the first morning bid from bc.
BidCollection bc;
Time t (12, 0, 0);
bc = bids;
for (int i = 0; i < x.size;)
{
if (bc.elements[i].bidPlacedAt < t)
removeElement (elements, size, i);
else
++i;
}

Then remove the remaining morning bid from bc.
bids is corrupted

Note that we have corrupted the original collection, bids
-
It thinks it has more (according to
size) bids than are left in the array -
The bids that it has are now changed
This should look very familiar!
Avoiding this Problem
We have already seen that, for this class, we need to implement our own copy constructor:
BidCollection::BidCollection (const BidCollection& bc)
: MaxSize (bc.MaxSize), size (bc.size)
{
elements = new Bid[MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
For all the same reasons, we will want to implement our own assignment operator.
3.2 Implementing Assignment
BidCollection& BidCollection::operator=
(const BidCollection& bc)
{
MaxSize = bc.MaxSize;
size = bc.size;
delete [] elements;
elements = new Bid[MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
return *this;
}
Why return this?
-
By tradition in C++, assignments can be chained:
a = b = c = 0;-
Works because compiler interprets this as
a = (b = (c = 0)); -
Not unlike
<<
-
-
The return value from
operator=allows the value to be assigned to the prior assignment in the chain.
Self-Assignment
When we do x = x we expect that nothing really changes.
Question: What would happen if we did
bids = bids;
using this assignment operator:
BidCollection& BidCollection::operator=
(const BidCollection& bc)
{
MaxSize = bc.MaxSize;
size = bc.size;
delete [] elements;
elements = new Bid[MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
return *this;
}
?
Self-Assignment – Really?
May seem an unlikely occurrence, but can often happen in a disguised form, e.g., during array processing,
bidSet[i] = bidSet[j];
- What if
i == j?
Coping with Self-Assignment
To allow for this possibility, most assignment operator functions check to see if the variable on the left (this) is at the same address as the variable on the right:
BidCollection& BidCollection::operator= (const BidCollection& bc)
{
if (this != &bc)
{
MaxSize = bc.MaxSize;
size = bc.size;
delete [] elements;
elements = new Bid[MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
return *this;
}
4 The Rule of the Big 3
A Question of Trust
-
When do we not trust the compiler-provided copy constructor?
-
When do we not trust the compiler-provided assignment operator?
-
When do we not trust the compiler-provided destructor?
-
When do we not trust the compiler-provided copy constructor?
- When we have pointers among our data members, and
- We don’t want to share the data we are pointing to
-
When do we not trust the compiler-provided assignment operator?
- When we have pointers among our data members, and
- We don’t want to share the data we are pointing to
-
When do we not trust the compiler-provided destructor?
- When we have pointers among our data members, and
- We don’t want to share the data we are pointing to
Notice a pattern?
The Rule of the Big 3
-
The copy constructor, assignment operator, and destructor are known as the Big 3.
-
The Rule of the Big 3 states:
If you provide your own version of any one of the Big 3, you should provide your own version of all three.
Providing the Big 3
-
The Bid, Bidder, Time, & Money ADTs: no change.
-
None of the data members are pointers, so we trust the compiler-generated versions.
-
-
BidCollection
#ifndef BIDCOLLECTION_H
#define BIDCOLLECTION_H
#include "bids.h"
#include <iostream>
class BidCollection {
int MaxSize;
int size;
Bid* elements; // array of bids
public:
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of bids
*/
BidCollection (int MaxBids = 1000);
// Big 3
BidCollection (const BidCollection&);
BidCollection& operator= (const BidCollection&);
~BidCollection ();
// Access to attributes
int getMaxSize() const {return MaxSize;}
int getSize() const {return size;}
// Access to individual elements
const Bid& get(int index) const {return elements[index];}
// Collection operations
void addInTimeOrder (const Bid& value);
// Adds this bid into a position such that
// all bids are ordered by the time the bid was placed
//Pre: getSize() < getMaxSize()
void remove (int index);
// Remove the bid at the indicated position
//Pre: 0 <= index < getSize()
/**
* Read all bids from the indicated file
*/
void readBids (std::string fileName);
// Print the collection
void print (std::ostream& out) const;
// Comparison operators
bool operator== (const BidCollection&) const;
bool operator< (const BidCollection&) const;
};
inline
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& out, const BidCollection& b)
{
b.print(out);
return out;
}
#endif
#include "bidcollection.h"
#include "arrayUtils.h"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of bids
*/
BidCollection::BidCollection (int MaxBids)
: MaxSize(MaxBids), size(0)
{
elements = new Bid [MaxSize];
}
// Big 3
BidCollection::BidCollection (const BidCollection& bc)
: MaxSize(bc.MaxSize), size(bc.size)
{
elements = new Bid [MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
BidCollection& BidCollection::operator= (const BidCollection& bc)
{
if (this != &bc)
{
delete [] elements;
size = bc.size;
MaxSize = bc.MaxSize;
elements = new Bid [MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
return *this;
}
BidCollection::~BidCollection ()
{
delete [] elements;
}
// Collection operations
void BidCollection::addInTimeOrder (const Bid& value)
// Adds this bid into a position such that
// all bids are ordered by the time the bid was placed
//Pre: getSize() < getMaxSize()
{
// Make room for the insertion
int toBeMoved = size - 1;
while (toBeMoved >= 0 &&
value < elements[toBeMoved]) {
elements[toBeMoved+1] = elements[toBeMoved];
--toBeMoved;
}
// Insert the new value
elements[toBeMoved+1] = value;
++size;
}
void BidCollection::remove (int index)
// Remove the bid at the indicated position
//Pre: 0 <= index < getSize()
{
removeElement (elements, size, index);
}
/**
* Read all bids from the indicated file
*/
void BidCollection::readBids (std::string fileName)
{
size = 0;
ifstream in (fileName.c_str());
int nBids;
in >> nBids;
for (int i = 0; i < nBids; ++i)
{
char c;
string bidderName;
double amount;
in >> bidderName >> amount;
Time bidPlacedAt;
bidPlacedAt.read (in);
string word, line;
in >> word; // First word of itemName
getline (in, line); // rest of item name
string itemName = word + line;
addInTimeOrder (Bid (bidderName, amount, itemName, bidPlacedAt));
}
}
// Print the collection
void BidCollection::print (std::ostream& out) const
{
out << size << "/" << MaxSize << "{";
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
out << " ";
elements[i].print (out);
out << "\n";
}
out << "}";
}
// Comparison operators
bool BidCollection::operator== (const BidCollection& bc) const
{
if (size == bc.size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
if (!(elements[i] == bc.elements[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool BidCollection::operator< (const BidCollection& bc) const
{
if (size == bc.size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (elements[i] < bc.elements[i])
return true;
else if (bc.elements[i] < elements[i])
return false;
// else keep going
}
// All of the elements are equal
return false;
}
else
return size < bc.size;
}
- BidderCollection:
#ifndef BIDDERCOLLECTION_H
#define BIDDERCOLLECTION_H
#include "bidders.h"
#include <iostream>
//
// Bidders Registered for auction
//
class BidderCollection {
int MaxSize;
int size;
Bidder* elements; // array of items
public:
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of items
*/
BidderCollection (int MaxBidders = 1000);
// Big 3
BidderCollection (const BidderCollection&);
BidderCollection& operator= (const BidderCollection&);
~BidderCollection ();
// Access to attributes
int getMaxSize() const {return MaxSize;}
int getSize() const {return size;}
// Access to individual elements
Bidder& get(int index) {return elements[index];}
// Collection operations
int add (const Bidder& value);
// Adds this bidder to the collection at an unspecified position.
// Returns the position where added.
//Pre: getSize() < getMaxSize()
void remove (int index);
// Remove the item at the indicated position
//Pre: 0 <= index < getSize()
int findBidder (std::string name) const;
// Returns the position where a bidde mathcing the given
// name can be found, or getSize() if no bidder with that name exists.
/**
* Read all items from the indicated file
*/
void readBidders (std::string fileName);
// Print the collection
void print (std::ostream& out) const;
// Comparison operators
bool operator== (const BidderCollection&) const;
bool operator< (const BidderCollection&) const;
};
inline
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& out, const BidderCollection& b)
{
b.print(out);
return out;
}
#endif
#include <iostream>
#include "arrayUtils.h"
#include <fstream>
#include "biddercollection.h"
using namespace std;
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of items
*/
BidderCollection::BidderCollection (int MaxBidders)
: MaxSize(MaxBidders), size(0)
{
elements = new Bidder [MaxSize];
}
// Big 3
BidderCollection::BidderCollection (const BidderCollection& bc)
: MaxSize(bc.MaxSize), size(bc.size)
{
elements = new Bidder [MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
BidderCollection& BidderCollection::operator= (const BidderCollection& bc)
{
if (this != &bc)
{
delete [] elements;
size = bc.size;
MaxSize = bc.MaxSize;
elements = new Bidder [MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
return *this;
}
BidderCollection::~BidderCollection ()
{
delete [] elements;
}
// Collection operations
int BidderCollection::add (const Bidder& value)
// Adds this bidder
//Pre: getSize() < getMaxSize()
{
addToEnd (elements, size, value);
return size - 1;
}
void BidderCollection::remove (int index)
// Remove the bidder at the indicated position
//Pre: 0 <= index < getSize()
{
removeElement (elements, size, index);
}
/**
* Read all bidders from the indicated file
*/
void BidderCollection::readBidders (std::string fileName)
{
size = 0;
ifstream in (fileName.c_str());
int nBidders;
in >> nBidders;
for (int i = 0; i < nBidders && i < MaxSize; ++i)
{
string nme;
double bal;
in >> nme >> bal;
Bidder bidder (nme, bal);;
add (bidder);
}
}
/**
* Find the index of the bidder with the given name. If no such bidder exists,
* return nBidders.
*/
int BidderCollection::findBidder (std::string name) const
{
int found = size;
for (int i = 0; i < size && found == size; ++i)
{
if (name == elements[i].getName())
found = i;
}
return found;
}
// Print the collection
void BidderCollection::print (std::ostream& out) const
{
out << size << "/" << MaxSize << "{";
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
out << " ";
elements[i].print (out);
out << "\n";
}
out << "}";
}
// Comparison operators
bool BidderCollection::operator== (const BidderCollection& bc) const
{
if (size == bc.size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
if (!(elements[i] == bc.elements[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool BidderCollection::operator< (const BidderCollection& bc) const
{
if (size == bc.size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (elements[i] < bc.elements[i])
return true;
else if (bc.elements[i] < elements[i])
return false;
// else keep going
}
// All of the elements are equal
return false;
}
else
return size < bc.size;
}
- ItemCollection ADT:
#ifndef ITEMCOLLECTION_H
#define ITEMCOLLECTION_H
#include "items.h"
#include <iostream>
class ItemCollection {
int MaxSize;
int size;
Item* elements; // array of items
public:
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of items
*/
ItemCollection (int MaxItems = 1000);
// Big 3
ItemCollection (const ItemCollection&);
ItemCollection& operator= (const ItemCollection&);
~ItemCollection ();
// Access to attributes
int getMaxSize() const {return MaxSize;}
int getSize() const {return size;}
// Access to individual elements
const Item& get(int index) const {return elements[index];}
// Collection operations
void addInTimeOrder (const Item& value);
// Adds this item into a position such that
// all items are ordered by the time at which the auction for the
// item ends.
//Pre: getSize() < getMaxSize()
void remove (int index);
// Remove the item at the indicated position
//Pre: 0 <= index < getSize()
/**
* Read all items from the indicated file
*/
void readItems (std::string fileName);
// Print the collection
void print (std::ostream& out) const;
// Comparison operators
bool operator== (const ItemCollection&) const;
bool operator< (const ItemCollection&) const;
};
inline
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& out, const ItemCollection& b)
{
b.print(out);
return out;
}
#endif
#include <iostream>
#include "arrayUtils.h"
#include <fstream>
#include "itemcollection.h"
//
// Items up for auction
//
using namespace std;
/**
* Create a collection capable of holding the indicated number of items
*/
ItemCollection::ItemCollection (int MaxItems)
: MaxSize(MaxItems), size(0)
{
elements = new Item [MaxSize];
}
// Big 3
ItemCollection::ItemCollection (const ItemCollection& bc)
: MaxSize(bc.MaxSize), size(bc.size)
{
elements = new Item [MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
ItemCollection& ItemCollection::operator= (const ItemCollection& bc)
{
if (this != &bc)
{
delete [] elements;
size = bc.size;
MaxSize = bc.MaxSize;
elements = new Item [MaxSize];
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
elements[i] = bc.elements[i];
}
return *this;
}
ItemCollection::~ItemCollection ()
{
delete [] elements;
}
// Collection operations
void ItemCollection::addInTimeOrder (const Item& value)
// Adds this item into a position such that
// all items are ordered by the time the item' auction ends
//Pre: getSize() < getMaxSize()
{
addInOrder (elements, size, value);
}
void ItemCollection::remove (int index)
// Remove the item at the indicated position
//Pre: 0 <= index < getSize()
{
removeElement (elements, size, index);
}
/**
* Read all items from the indicated file
*/
void ItemCollection::readItems (std::string fileName)
{
size = 0;
ifstream in (fileName.c_str());
int nItems;
in >> nItems;
for (int i = 0; i < nItems; ++i)
{
Item item;
item.read (in);
addInTimeOrder (item);
}
}
// Print the collection
void ItemCollection::print (std::ostream& out) const
{
out << size << "/" << MaxSize << "{";
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
out << " ";
elements[i].print (out);
out << "\n";
}
out << "}";
}
// Comparison operators
bool ItemCollection::operator== (const ItemCollection& ic) const
{
if (size == ic.size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
if (!(elements[i] == ic.elements[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool ItemCollection::operator< (const ItemCollection& ic) const
{
if (size == ic.size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
if (elements[i] < ic.elements[i])
return true;
else if (ic.elements[i] < elements[i])
return false;
// else keep going
}
// All of the elements are equal
return false;
}
else
return size < ic.size;
}